Select Jupyter as the plugin then select an option for Python Version and Type within the Application Parameters.
The Jupyter application will launch in a browser from your home folder on the selected system. The Jupyter Notebook and JupyterLab applications have a similar interface with JupyterLab offering more features and an enhanced interface.
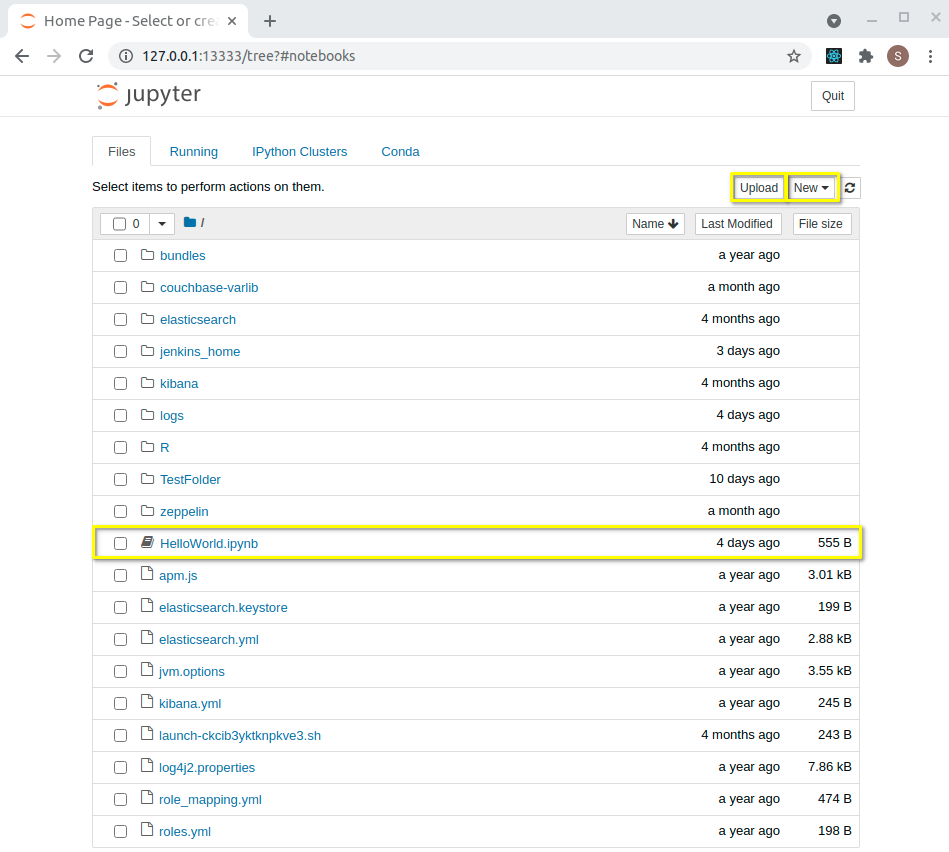
When using Jupyter Notebook, start a new notebook using the “new” tab, upload an existing notebook using “upload”, or open an existing notebook on the system.

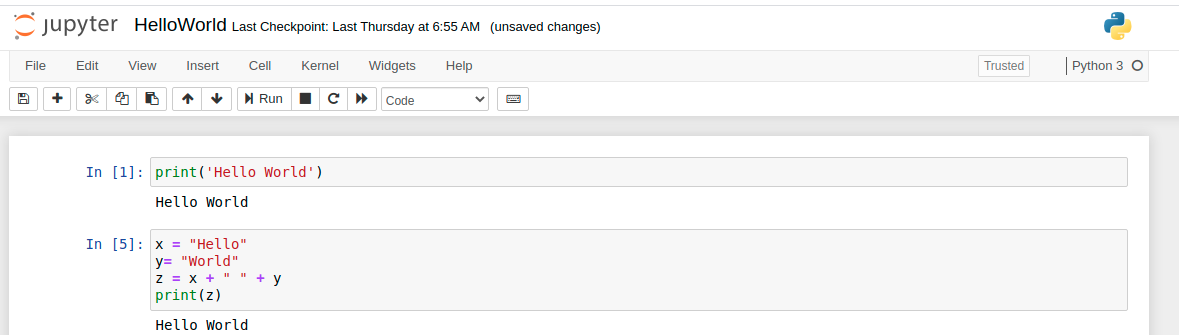
Jupyter supports over 40 programming languages, including Python, R, Julia, and Scala. Below is a simple demonstration in Python.
For more information on how to use the Jupyter family of products, please visit jupyter.org
The Jupyter application includes Conda with Python 2.7, 3.6, 3.7 & 3.8.
| Node Type | CPU | GPU |
|---|---|---|
| Python | 3.6 / 3.7 / 3.8 | 3.6 / 3.7 / 3.8 |
| CudaToolKit | N/A | 11.0.221 |
| cuDNN | N/A | 8.0.4 |
| TensorFlow | 2.4.1 | 2.4.0 |
| PyTorch | 1.7.0 | 1.7.0 |
Option 1: Userspace Pip
For most Python packages a user space pip is a great option. The command can be executed from the Jupyter Terminal pip install --user MODULE-NAME (e.g., pip install --user camelcase). This will side-effect the .local directory of your user’s home directory on the remote machine and will make that package availabe to all Python instances.
Pros:
Cons:
Option 2: Personal Conda Environment
Command-line Method: Run
$PROJECTS_HOME/INFINITE/default-plugin-channel/apps/conda-jupyter/conda-bin3.8/conda-bashJupyter Method: Open the terminal in Jupyter
Create a custom conda environment (in the below example the environment’s name is myenv)
conda create --name myenv
If you want to use the environment in juptyer – start a Jupyter session from iLauncher – go to the terminal from Jupyter, run the below command and refresh the page
python -m ipykernel install --user --name myenv --display-name "Python (myenv)"
Pros:
Cons: